
Plywood is a material used in many applications, from furniture making to construction. It stands out due to its durability, strength, and versatility. However, one of the most critical aspects of using plywood in projects is knowing how much weight can plywood hold. Whether you are using plywood for flooring, shelving, or structural support, understanding its weight-bearing capacity is essential to ensure the safety and stability of your project. If you overload plywood, you could risk failure, which may lead to costly damage and safety hazards.
In this article, we will thoroughly explore how much weight can plywood hold, delving into the factors that influence its weight capacity, methods for calculating its load-bearing ability, and the practical applications of plywood in everyday construction. This detailed guide will give you the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about plywood for all types of projects.
What is Plywood?
Before diving into its weight-bearing capabilities, let’s first understand what plywood is and how it is made. Plywood is an engineered wood product consisting of several thin layers (plies) of wood veneer glued together. The grain of each layer runs in alternating directions, which enhances the plywood’s strength and stability. The materials used, the number of layers, and the type of wood all contribute to the final product’s strength, flexibility, and ability to hold weight.
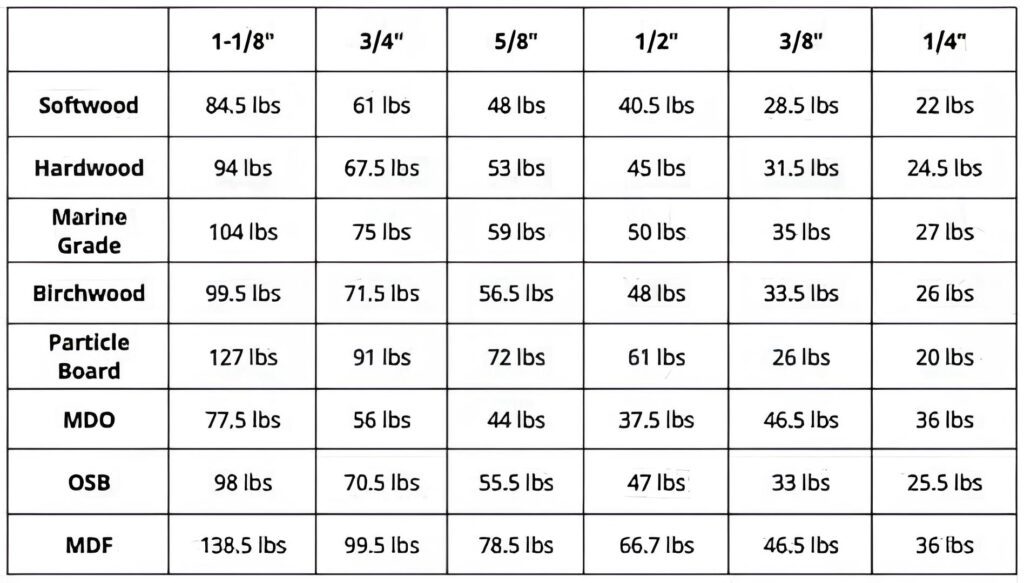
Types of Plywood
- Softwood Plywood: This type of plywood is made from softer woods like pine, fir, and spruce. It’s typically used for general construction purposes, such as wall sheathing, subflooring, and structural supports. Softwood plywood is highly cost-effective and works well for load-bearing applications where extreme strength isn’t needed.
- Hardwood Plywood: Hardwood plywood is made from durable hardwoods like oak, maple, and birch. This type of plywood is generally used for finer applications, such as cabinetry, furniture, and decorative projects. Hardwood plywood tends to be denser and stronger, which allows it to hold more weight than softwood plywood.
- Marine Plywood: Designed specifically for use in environments exposed to moisture, marine plywood is made from waterproof glue and higher-grade veneers. It is commonly used in boat building and other projects where the material must withstand high humidity and water exposure. While marine plywood can support substantial weight, its primary strength lies in its resistance to water damage.
The type of plywood you choose for a project will greatly affect how much weight it can hold. Softwood plywood may not hold as much weight as hardwood plywood, but it’s still highly useful for many general applications.
Factors Affecting Plywood’s Weight Capacity
To understand how much weight can plywood hold, it is crucial to consider a variety of factors that influence its load-bearing ability. These factors include the thickness of the plywood, the type of wood used, the grade of plywood, and the number of layers in the material. Each of these elements can either increase or decrease how much weight plywood can carry.
Thickness of Plywood
One of the most influential factors in determining how much weight plywood can hold is its thickness. Thicker plywood naturally has more material to support weight, making it more capable of handling larger loads. For example, a 3/4-inch thick plywood sheet will support more weight than a 1/4-inch sheet. Generally, plywood thickness can range from 1/8 inch to 1 1/4 inches or more, and the thicker the plywood, the higher its weight capacity.
For flooring applications, for example, plywood typically ranges between 1/2 inch and 3/4 inch in thickness, depending on the expected load. In shelving or furniture projects, thinner plywood might suffice, but for heavy-duty or structural uses, thicker plywood should always be used to handle higher weight.
Wood Type and Quality
The type of wood used to manufacture plywood plays a crucial role in determining how much weight it can withstand. Hardwoods such as oak, maple, and walnut are stronger and denser than softwoods like pine or fir. As a result, hardwood plywood can generally support more weight and endure more strain compared to softwood plywood.
In addition to the wood species, the overall quality of the wood also affects how much weight can plywood hold. If the plywood is made from low-quality wood, such as wood with numerous knots, defects, or inconsistent grain, it will have a reduced ability to bear weight. High-quality wood, free from defects and with consistent grain patterns, will provide superior load-bearing performance.
Grade of Plywood
Plywood is graded based on its quality, which directly impacts its strength and load-bearing capacity. Grades typically range from A to D, with A being the highest grade. Higher-grade plywood has fewer defects, is smoother, and is more consistent in structure, meaning it can support more weight. For example:
- Grade A Plywood: Free from visible defects, smooth, and highly durable. It’s ideal for fine furniture and cabinetry, as well as applications where strength and appearance are essential.
- Grade B Plywood: Has some visible imperfections, but still strong enough for general construction and structural support. It typically has a smooth surface but may contain small knots.
- Grade C and D Plywood: These grades are used for industrial or rough applications, such as subflooring or wall sheathing. These grades contain more visible defects, but are still functional in non-visible areas where aesthetics are not a concern.
The grade of plywood you select for your project directly correlates to how much weight it can hold. Higher-grade plywood will generally be able to support more weight than lower-grade plywood.

Layer Structure
Plywood is made by bonding together multiple layers of thin wood veneers. These layers are called «plies,» and the number of plies in the plywood directly impacts its strength and load-bearing ability. A sheet of plywood with more plies will be stronger and capable of supporting more weight than one with fewer plies.
Most commercial plywood ranges from 3-ply to 13-ply sheets, with 5-ply and 7-ply being common for residential construction. The more plies, the greater the strength and capacity of the plywood, as the layers work together to resist bending and warping.
Orientation of Grain
The way the wood grains are oriented in plywood also influences how much weight can plywood hold. In plywood, the grain direction alternates with each layer, which improves the material’s strength. This cross-grain structure prevents the plywood from bending or warping under pressure, allowing it to handle higher loads.
In some cases, the direction of the grain relative to the intended load can be an important consideration. For example, when installing plywood as flooring or for structural applications, it’s critical to align the grain in a direction that will best support the weight distribution of the load. If the grain is not oriented properly, plywood may not hold as much weight as it otherwise could.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors like moisture, temperature, and humidity can affect the strength and weight-bearing capacity of plywood. Plywood that is exposed to excessive moisture can weaken over time, causing the glue to break down and the wood to swell or warp. In high-humidity areas, plywood may lose its structural integrity and may not hold as much weight.
To ensure that plywood can support the intended weight, it is essential to consider the environment in which it will be used. For instance, using marine plywood or a treated plywood that is resistant to moisture will enhance the material’s ability to bear weight in damp environments. Similarly, keeping plywood away from extreme temperature fluctuations or damp conditions will help preserve its strength.

Understanding Plywood Load-Bearing Capacity
Knowing how to calculate the weight capacity of plywood is essential for its effective use in different applications. While some manufacturers provide weight ratings, understanding the general guidelines for calculating plywood’s load-bearing capacity is valuable for anyone working with the material.
Weight Capacity in Different Applications
The amount of weight plywood can hold will vary depending on its intended application. For example:
- Flooring: When plywood is used for flooring, it must support dynamic loads, such as the movement of people and furniture, as well as static loads, such as heavy appliances. A typical 3/4-inch plywood sheet for flooring can hold up to 50 to 70 pounds per square foot when properly supported. For higher weight-bearing needs, thicker plywood or additional support beams may be required.
- Shelving: When used in shelving units, plywood must support the weight of stored items, such as books or boxes. For a typical 3/4-inch thick shelf, it can hold anywhere from 50 to 100 pounds per square foot, depending on the distance between the shelf supports.
- Structural Support: Plywood used in structural applications like wall sheathing, roofs, and floors must withstand far heavier loads. A properly installed 3/4-inch thick plywood wall can hold significant weight, especially when combined with framing or other support materials.
Calculating Maximum Weight Plywood Can Hold
A simple formula often used to calculate the maximum weight plywood can support is based on the thickness of the material, its grade, and the span between supports. These factors are combined to determine the overall load-bearing capacity of the plywood.
For example, a general formula might look like this:Weight Capacity=Thickness×Support Span×Grade Factor\text{Weight Capacity} = \text{Thickness} \times \text{Support Span} \times \text{Grade Factor}Weight Capacity=Thickness×Support Span×Grade Factor
This equation provides a starting point, but professional guidelines and specific weight charts are more precise for real-world applications. Consulting detailed load tables or manufacturer specifications is often necessary when working with plywood for critical applications.
Standard Weight Limits for Various Plywood Grades and Types
Different grades and types of plywood have varying weight capacities. As a general rule:
- 1/4-inch plywood: Can hold approximately 40 to 50 pounds per square foot.
- 1/2-inch plywood: Can hold around 60 to 70 pounds per square foot.
- 3/4-inch plywood: Can support between 100 to 120 pounds per square foot, depending on the grade and the span.
For heavier loads, thicker plywood may be necessary, or additional reinforcement methods like beams, braces, or metal supports should be considered.

Testing Plywood’s Strength
Manufacturers determine the weight-bearing capacity of plywood through several testing methods, such as bending tests, shear strength tests, and load testing under real-world conditions.
Bending Tests
Bending tests involve applying increasing amounts of force to plywood to see at what point it begins to bend or break. These tests help determine the maximum load the plywood can handle before failure. This kind of test is valuable for understanding how much weight can plywood hold when subjected to pressure over time.
Shear Strength Tests
Shear strength tests measure how well plywood can resist internal forces that try to slide one layer past another. This is particularly important in structural applications where the plywood is exposed to forces trying to push or pull the material in different directions. By measuring the shear strength, manufacturers can better understand how much weight plywood can bear in structural settings.
Load Testing in Real-World Applications
To simulate real-world conditions, plywood is also subjected to load tests on construction sites or in controlled environments. These tests often involve applying weight to plywood to see how it reacts when used in actual applications, such as flooring, shelving, or as part of a building structure.

Common Applications and Load Considerations
Plywood is used in various industries, including construction, furniture making, and vehicle design. Its weight capacity plays a major role in determining which projects are suitable for plywood and what thickness, grade, and type are required.
Flooring
How much weight can plywood flooring hold? For most residential applications, 3/4-inch plywood is typically used for subflooring and can bear approximately 50 to 70 pounds per square foot. For commercial or industrial applications, heavier-duty plywood might be necessary.
Shelving and Furniture
Plywood shelves and furniture units have varying weight limits depending on thickness and support. A typical plywood shelf can hold 50 to 100 pounds per square foot, but increasing the thickness or adding supports can allow for greater weight capacity.
Structural Support
In structural applications such as wall sheathing and roofing, plywood’s weight capacity is much higher. Properly installed 3/4-inch plywood sheets used in walls or roofs can support significant loads, especially when combined with additional framing or metal supports.
Other Uses
Plywood also plays a role in heavy-duty applications, such as in boats, trucks, or industrial machinery. For example, marine plywood is used to build boats that must withstand exposure to water, while vehicle manufacturers use plywood for components that must support heavy loads. In these contexts, plywood must be able to hold up under substantial weight while maintaining its durability in challenging environments.

How to Enhance Plywood’s Weight-Bearing Capacity
If the plywood you are working with isn’t sufficient for the weight you plan to bear, there are methods you can use to increase its load-bearing capacity.
Reinforcement Methods
One common method to increase plywood’s weight capacity is by reinforcing it with additional layers or structural supports. Adding another layer of plywood or installing support beams underneath can distribute the weight more evenly and prevent bending or breaking.
Combining with Other Materials
Using plywood in combination with other materials, such as steel brackets or wooden beams, can also enhance its ability to hold weight. By creating a hybrid structure, you increase the strength of the overall setup, allowing it to support greater loads.
Proper Installation Techniques
Ensuring plywood is properly installed with the correct spacing of supports, correct grain orientation, and secure attachment will maximize its weight capacity. For example, making sure plywood is supported at proper intervals ensures that weight is evenly distributed, reducing the chance of failure.

Safety Considerations and Limitations
Exceeding the weight capacity of plywood can lead to disastrous results. Overloaded plywood can warp, crack, or even break, posing safety risks. Therefore, it’s critical to always work within the specified weight limits for the material.
Signs of Overload
If you notice that plywood begins to bow, crack, or show signs of warping, it is likely under excessive weight. These signs are early indicators that the plywood may no longer be safe to use.
Best Practices for Ensuring Safety
To avoid overload, always adhere to manufacturer guidelines, use appropriate thicknesses for your project, and ensure proper support structures are in place. Reinforcing plywood with additional materials or using thicker plywood may also be necessary for heavy-duty applications.
Conclusion
Plywood is a strong, reliable material with varying weight-bearing capacities depending on its type, thickness, and grade. By carefully considering these factors and understanding how much weight plywood can hold, you can ensure your projects are safe and stable. Always consult manufacturers’ specifications, follow best practices for installation, and use reinforcement methods when necessary to ensure your plywood can support the weight it’s designed to hold. Whether you’re working on a home improvement project or building a commercial structure, knowing how much weight can plywood hold will guide you to make the right decisions for your project’s success.